Automated Ball Valves
What Are Automated Ball Valves and How Do They Enhance Flow Control?
|
|
What Are Automated Ball Valves?Automated ball valves are valve systems that use an actuator (electric, pneumatic, or hydraulic) to automate the opening and closing of the valve. These valves are designed for precise flow control in a wide variety of applications, from water treatment plants to chemical processing facilities. Why Choose Automated Ball Valves?Automated ball valves offer precise, repeatable control, ensuring consistent performance without the need for manual adjustments. Whether managing high-pressure systems, corrosive fluids, or critical shutoff applications, they provide fast actuation and reliable sealing, reducing the risk of leaks and operational downtime. More importantly, they seamlessly integrate into automated control systems, allowing for remote operation, predictive maintenance, and optimized process efficiency. For companies looking to improve safety, reliability, and long-term cost savings, automated ball valves are a smart investment that delivers both performance and peace of mind. |
Key Benefits of Automated Ball Valves
 |
 |
 |
 |
Precise Flow Control |
Increased Efficiency and Reduced Downtime |
Reliability in Harsh Environments |
Cost-Effective Operations |
How Do Automated Ball Valves Work?
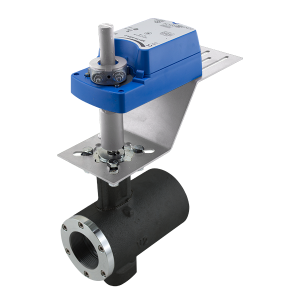
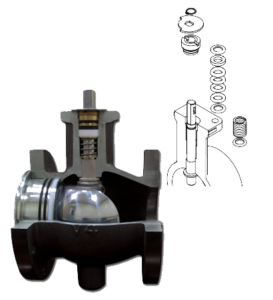
Structure and DesignAutomated ball valves use a rotating ball with a hole (bore) through its center to control fluid flow. When the actuator rotates the ball 90 degrees, it either aligns the bore with the pipeline for full flow or blocks it to stop flow. These valves consist of a valve body, ball, stem, seats, and actuator (electric, pneumatic, or hydraulic). The actuator automates the operation, allowing remote or programmed control. Seals and seats ensure tight shutoff, making them ideal for on/off applications in industries like oil & gas, water treatment, and chemical processing. Their design offers low torque operation, quick response time, and high durability. |
 |
 |
Actuator IntegrationAutomated ball valves integrate an actuator to enable remote or automatic control of fluid flow. The actuator, which can be electric, pneumatic, or hydraulic, is mounted on the valve stem and connected via an ISO-standard flange or bracket for secure attachment. It converts electrical, air, or hydraulic energy into rotational motion, turning the ball 90 degrees to open or close the valve. Many actuators include positioners, solenoids, or feedback sensors for precise control and monitoring. This integration allows for fast, reliable operation, making automated ball valves essential in industries requiring high efficiency, safety, and automation. |
Types of Actuators Used in Automated Ball Valves
Most Common Types of Ball Valves
| Full Port Ball Valves |  |
DescriptionStandard ball valves, specifically full port ball valves, feature an oversized ball and bore that match the inner diameter of the pipeline, ensuring unrestricted flow with minimal pressure drop. This design reduces turbulence and allows for efficient fluid transfer. Constructed from materials like stainless steel, brass, or PVC, these valves offer high durability, corrosion resistance, and leak-proof sealing. Operated manually or with an actuator, full port ball valves provide quick quarter-turn operation for reliable on/off control in various systems. |
ApplicationsFull port ball valves are widely used in industries where high flow capacity and minimal pressure loss are critical. They are commonly found in oil and gas pipelines, chemical processing, water treatment plants, and HVAC systems. Their ability to handle viscous fluids, slurries, and gases makes them ideal for applications requiring efficient flow control and long-term reliability. Additionally, they are frequently used in food and beverage processing, where maintaining unobstructed flow and sanitary conditions is essential. |
||
| Reduced Port Ball Valves |  |
DescriptionA reduced port ball valve, also known as a reduced bore ball valve, has a smaller flow passage than the pipeline diameter. Unlike full port valves, where the bore matches the pipe size, a reduced port valve narrows the flow path, creating a venturi effect that slightly restricts flow and increases velocity. These valves are designed with a compact body, making them lighter and more cost-effective than full port alternatives. While they introduce some pressure drop, they still offer efficient shutoff, low torque operation, and durability in various fluid control systems. |
ApplicationsReduced port ball valves are widely used in industries where minor pressure loss is acceptable and cost efficiency is a priority. They are commonly found in HVAC systems, water distribution, oil and gas pipelines, and general industrial processes. These valves are particularly useful in applications where space and weight constraints are important, such as skid-mounted systems or tight piping configurations. Additionally, they work well in gas and liquid flow control where a full bore valve is unnecessary, providing a reliable and economical solution for automated or manual flow regulation. |
||
| V-Port Ball Valves |  |
DescriptionV-Port ball valves are a specialized type of control valve featuring a V-shaped ball or seat that allows for precise flow regulation. Unlike standard ball valves, which operate in a simple on/off manner, V-Port valves provide modulating control, enabling a more linear flow characteristic. The “V” notch design creates a more controlled and stable flow rate, reducing turbulence and cavitation. These valves are available in different V angles (e.g., 30°, 60°, 90°) to suit varying flow control requirements. Made from materials like stainless steel or carbon steel, they offer durability and reliability in demanding applications. |
ApplicationsV-Port ball valves are widely used in industries requiring accurate flow control and throttling, such as chemical processing, water treatment, HVAC, pulp and paper, and food & beverage. They are ideal for controlling the flow of liquids, gases, and slurries, especially in systems where precise pressure and flow regulation are critical. In steam and high-pressure applications, their ability to handle high velocities and minimize wear makes them a preferred choice over traditional globe or butterfly valves. Their automation compatibility allows integration with actuators for remote and precise control in industrial processes. |
||
| Trunnion Ball Valves |
DescriptionTrunnion ball valves are a type of ball valve designed for high-pressure and large-diameter applications. Unlike floating ball valves, they feature a trunnion-mounted ball, which means the ball is held in place by additional mechanical anchoring at the top and bottom. This design reduces excessive torque and distributes pressure more evenly, allowing for smoother operation. The valve includes spring-loaded or piston seats, ensuring a tight seal even at low pressures. Trunnion ball valves are commonly available in two-piece or three-piece body constructions, providing flexibility for maintenance and installation. |
|
ApplicationsDue to their ability to handle high-pressure and high-flow conditions, trunnion ball valves are widely used in industries such as oil & gas, petrochemicals, power plants, and water treatment. They are commonly installed in pipelines, transmission systems, and refining processes where reliable shutoff and minimal pressure drop are crucial. Their durability and ability to maintain a tight seal under extreme conditions make them ideal for handling natural gas, crude oil, and other critical fluids in both onshore and offshore applications. |
||
| Floating Ball Valves |
DescriptionA floating ball valve is a type of quarter-turn valve where the ball is not fixed to the stem but instead “floats” between two seats. When the valve is closed, fluid pressure pushes the ball against the downstream seat, creating a tight seal that prevents leakage. These valves typically feature soft seats (PTFE, TFM, or other polymers) for excellent sealing performance. Floating ball valves are commonly used in low to medium pressure applications and are available in two-piece, three-piece, and top-entry designs for easy maintenance and versatility. |
|
| Floating ball valves are widely used in oil & gas, chemical processing, water treatment, and HVAC systems due to their compact size, reliable shutoff, and ease of operation. They are ideal for liquids and gases in applications where tight sealing and minimal leakage are critical. Industries utilize them for pipeline isolation, process control, and safety shut-off systems. However, for high-pressure applications, a trunnion-mounted ball valve is often preferred to handle the additional force on the ball. | ||
| Multi-way Ball Valves |  |
DescriptionMulti-way ball valves are designed to control flow in multiple directions using a ball with multiple ports (typically 3-way or 4-way configurations). Unlike standard two-way ball valves that allow only open or close functions, multi-way valves can divert, mix, or distribute fluid through different pathways. These valves feature L-port or T-port ball designs, enabling various flow patterns. Constructed from materials like stainless steel, brass, or PVC, they provide durability, corrosion resistance, and high-pressure handling, making them versatile for complex piping systems. |
ApplicationsMulti-way ball valves are widely used in fluid mixing, distribution, and diversion applications across industries. In the chemical and pharmaceutical sectors, they help in blending different fluids. In HVAC and water treatment systems, they enable flow switching between multiple sources or outlets. In oil and gas processing, they efficiently manage fuel or lubricant distribution. Their ability to streamline piping configurations reduces space, installation time, and potential leak points, making them a preferred choice in automated and manual fluid control systems. |